Acute otitis media guidelines 2016
11 min readAcute otitis media guidelines 2016
It’s been seven years and two years since publication of two key acute otitis media treatment recommendations, the drug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae
Acute otitis media — Acute otitis media (AOM) is an acute illness marked by the presence of middle ear fluid and inflammation of the mucosa that lines the middle ear space . The infection is often caused by obstruction of the eustachian tube, which results in fluid retention and suppuration of retained secretions.
Question Acute otitis media is one of the most common infections in childhood. Routine prescription of The 2016 Canadian Paediatric Society guidelines suggest
Guideline Summary Nicole Le Saux, Immunization Committee. Paediatr Child Health 2016;21(1) of Acute Otitis Media in Children Six Months of Age and Older”.
2014-02-28 · Two-thirds of all children have an episode of acute otitis media An S2 guideline for the treatment of acute purulent otitis media is
2 Minute Medicine. Specialties. All [Policy Statement] New guidelines for pediatric acute otitis media released. March 4, 2013 2 Minute Medicine.
Guidelines 2016 General Notes Identification and management of sepsis in Primary Care 3 4 9 11 Meningitis and Meningococcal Disease Acute otitis media 21
Effective Treatment for Acute Otitis Externa. Meghan June 01, 2016. rare since the introduction of antibiotics for the treatment of acute otitis media,
What is acute otitis media? – at least one symptom or finding indicative Diagnosis and Management of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis: 2013 AAP Guideline – Prepared for
Otitis Media, Tympanostomy Tubes, and Clinical Practice Guidelines from 2013 may reduce pain during episodes of acute otitis media and can allow treatment
Guidelines by Alphabetical Listing. Otitis Media: Otitis Media – Acute Otitis Media & Otitis Media with Effusion For the latest updates on BC Guidelines,
YouTube Embed: No video/playlist ID has been supplied
Acute otitis media Guidelines – pediamcu.com
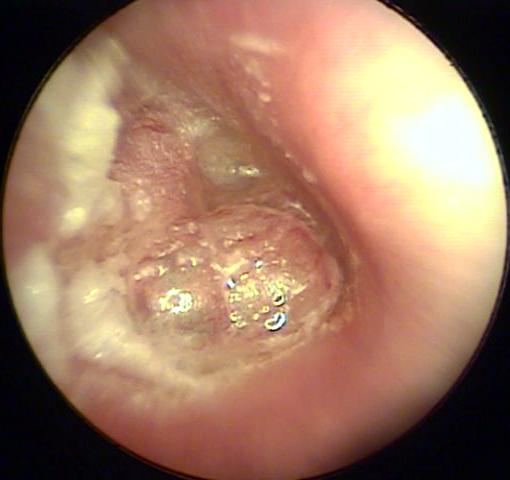
Acute Otitis Media SUMMARY – PedsCases
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media abstract This evidence-basedclinical practiceguideline isarevision of the2004
Background Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common childhood disease, with an enormous economic and healthcare-related burden. Guidelines and consensus papers for AOM diagnosis and management were published in many countries. Our objective was to study the differences and similarities between these protocols in developing and developed countries.
Systemic corticosteroids for acute otitis media in children. Acute otitis media clinical practice guideline defines AOM as an “acute onset of middle ear
The NICE guideline Otitis media (acute): Infectious Diseases and Immunization Committee (2016) Management of acute otitis media in children six months of age and
Acute otitis media Clinical pathways or guidelines (2) recommendations for the treatment and management of acute otitis media. Published online: October 2016.
Otitis media with effusion (OME) The presence of fluid in the middle ear without signs or symptoms of acute ear infection. Chronic OME OME persisting for 3 mo from the date of onset (if known) or from the date of diagnosis (if onset is unknown). Acute otitis media (AOM) The rapid onset of signs and symptoms of inflammation of the middle ear.
Acute Otitis Media in children is a very common ear infection caused by bacterial or viral infection. Read about Acute Otitis Media in children and ear infections
Complications of Acute Otitis Media Red flags . Acute otitis media (AOM) in the presence of: Sepsis with post auricular swelling; Cranial nerve palsy
Evidence-based information on guidelines of otitis media from hundreds of of the 2004 acute otitis media (AOM) guideline from the 01 August 2016.
Evidence-based recommendations on an antimicrobial prescribing strategy for acute otitis media 2016). More common complications of acute guideline on

Clinical Practice Guideline: Otitis Media with Effusion (Update) Otolaryngology– Head and Neck Surgery 2016, Vol. 154(1S) Acute otitis media
Shin JJ.Antibiotics administered for acute otitis media have modest benefits and adverse effects BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine 2016 ;21; 181 ( Abstract ) Otitis Media : Acute Otitis Media ( AOM ) and Otitis Media with Effusion ( OME ) BC Guidelines. ca Otitis Medua ( acute ) : antimicrobial prescribing NICE guideline March 2018 BMJ Best Practice Acute Otitis Media Most cases of otitis media should not …
Acute Otitis Media Red flags . Acute Unwell young children with discharging ears (acute suppurative otitis media) Acute Otitis Media. NICE Guideline 69.
Recurrent acute otitis media Guideline The Diagnosis and Management of for Acute Otitis Media in Young Children. N Engl J Med 2016; 375
Acute otitis media guidelines in selected developed and developing countries: uniformity and diversity Sharon Ovnat Tamir,1 Shay Shemesh,1 Yahav Oron,1 Tal Marom2
Acute otitis media Society guideline links: Acute otitis media and otitis media with Treatment for Acute Otitis Media in Young Children. N Engl J Med 2016;
Acute otitis media (AOM) is an ear infection common caused by bacterial or viral infection. Acute Otitis Media in Adults is rare. Read about Acute Otitis Media in Adults
Diagnosis requires acute onset and an abnormal ear examination with signs of middle ear inflammation and middle ear effusion. Avoid the routine use of antibiotic treatment for acute otitis media. Background. Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common problem in early childhood . 75% of children have at least one episode by school age
Management of acute otitis media in children six months Health. 2016 Jan-Feb health/practitioner-professional-resources/bc-guidelines/otitis-media
After acute otitis media, EBM Guidelines. Dec 16, 2016 • Latest change Dec 16, 2016. Tuomas Klockars and Aino Ruohola. Table of contents.

The guideline, Otitis Media with Effusion, was updated by the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgeons and endorsed by the American Academy of Family Physicians. Key Recommendations. Pneumatic otoscopy should be used as the primary diagnostic method for otitis media with effusion (OME) in a child with otalgia, hearing loss, or both.
2016 edition. Editorial committee Acute otitis media (AOM) These guidelines’ primary objective is to cure an individual patient of his disease, and to
Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common complication of an acute respiratory infection (ARI); it mostly affects children aged six to 12 months (Lieberthal 2013; SACHCN 2014).
ABSTRACTNew guidelines for managing acute otitis media include stricter criteria for properly diagno
The guideline was published as a supplement in the February 2016 issue of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. The purpose of this multidisciplinary guideline is
OBJECTIVE: This update of a 2004 guideline codeveloped by the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American Academy of Family Physicians, provides evidence-based recommendations to manage otitis media with effusion (OME), defined as the presence of fluid in the middle ear without signs or symptoms of acute ear …
ANMC Pediatric Acute Otitis Media (AOM) Treatment Guidelines Diagnosis Criteria Severe Symptoms Observation Criteria ANMC GAS Pharyngitis Guideline 2016 Author:
Antibiotic choice for acute otitis media 2018. acute otitis media (AOM). The guidelines of the American Academy of Pediatrics It showed that by end of 2016,
Management of acute otitis media in children six months of age and older. Paediatr Child Health 2016;21(1):39-44. Abstract. Acute otitis media (AOM)
Antibiotic therapy for children with acute otitis media
There is still some debate whether antibiotics influence the short term outcome of acute otitis media. erythromycin is an alternative for penicillin allergic patients
The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM is an infection of abrupt onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present.
Cite this article: Otitis Media: New Guideline Includes Screening At-Risk Kids – Medscape – Feb 04, 2016. Authors and Disclosures. Authors and Disclosures Journalist
Acute otitis media – Guidelines PediaMCU. February 16, 2016. Clinical practice guideline: the diagnosis and management of acute otitis media .
The following was adapted from the Canadian Paediatric Society’s statement on the “Management of Acute Otitis Media”. Please see the full statement for the full
Acute Otitis Media Guidelines in Selected Developed and Developing Countries: Uniformity and Diversity. 2016 2017 102: 450-457 originally
Comparison of otitis media with effusion (top) and acute otitis media (bottom). The left images show the appearance of the eardrum on otoscopy, and the right images depict the middle ear space. For otitis media with effusion, the middle ear space is filled with mucus or liquid (top right).
2016-03-15 · Richard M. Rosenfeld, MD, MPH discusses OME – What it is, who it affects and information about the updated clinical practice guideline.
New Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Otitis to primary care clinicians for the management of uncomplicated acute otitis media in children ages 2 – puersit mp3 player user manual Low quality evidence indicated that children treated with oral antibiotics were less likely to have acute otitis media (ear infection) episodes (CENTRAL 2016,
The most common type of ear infection is called otitis media. Acute otitis media and otitis for acute otitis media in young children. N Engl J Med. 2016
Acute Infection Guideline Summary TRIC 2016-17 Reference Articles Otitis Media: 1. Lieberthal AS et al. The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media.
… 2016. doi: 10.1001 on current care guidelines: acute otitis media Follow-up in Children With Acute Otitis Media Initially Managed Without Antimicrobials.
2018-04-13 · In the United States, acute otitis media Acute Otitis Media Guidelines. Pediatrics. 2016 Mar 28.
Acute otitis media — entsho.com
Innovative technologies in diagnosing acute otitis media

ANTIMICROBIAL PRESCRIBING GUIDELINES IN GENERAL PRACTICE
PPT – Acute Otitis Media PowerPoint presentation free to
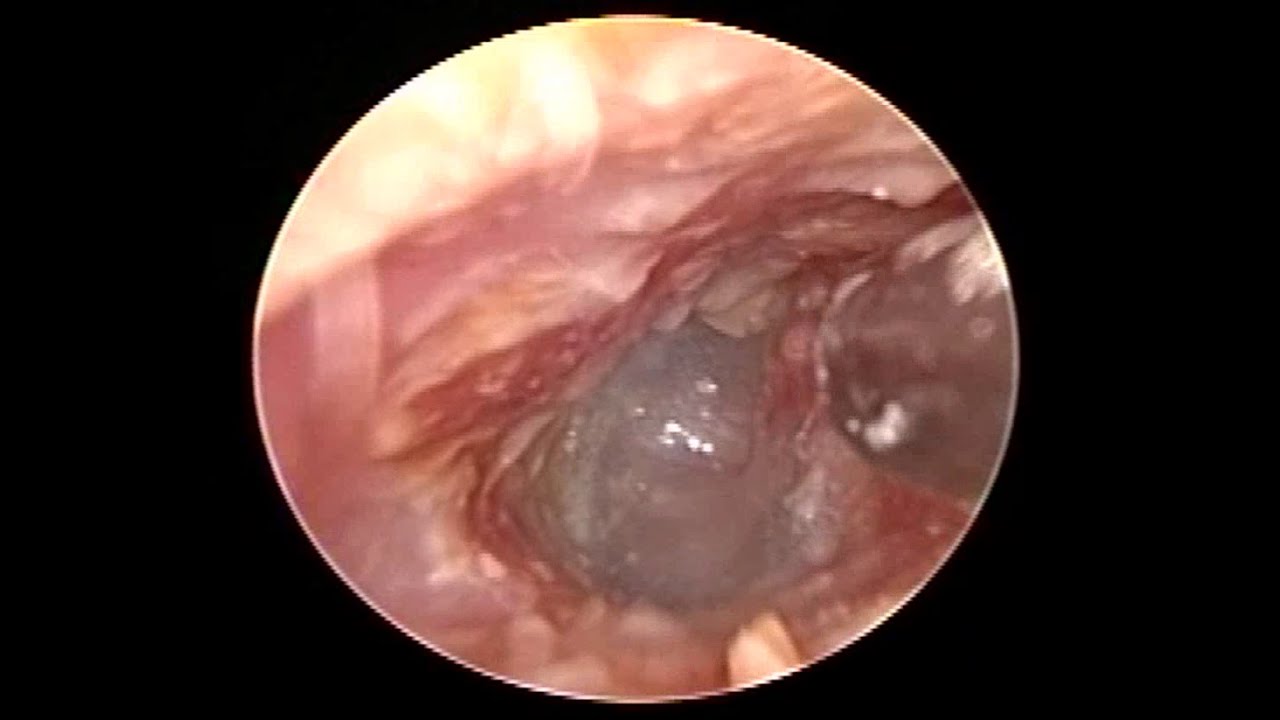
Acute Otitis Media ( AOM ) A4medicine.com
Updated Clinical Practice Guideline Otitis Media with


–


YouTube Embed: No video/playlist ID has been supplied
Acute otitis media — entsho.com
Antibiotic therapy for children with acute otitis media
Cite this article: Otitis Media: New Guideline Includes Screening At-Risk Kids – Medscape – Feb 04, 2016. Authors and Disclosures. Authors and Disclosures Journalist
Low quality evidence indicated that children treated with oral antibiotics were less likely to have acute otitis media (ear infection) episodes (CENTRAL 2016,
ANMC Pediatric Acute Otitis Media (AOM) Treatment Guidelines Diagnosis Criteria Severe Symptoms Observation Criteria ANMC GAS Pharyngitis Guideline 2016 Author:
Recurrent acute otitis media Guideline The Diagnosis and Management of for Acute Otitis Media in Young Children. N Engl J Med 2016; 375
Acute Otitis Media Red flags . Acute Unwell young children with discharging ears (acute suppurative otitis media) Acute Otitis Media. NICE Guideline 69.
Effective Treatment for Acute Otitis Externa Pharmacy Times
antibiotics in acute otitis media General Practice Notebook
Antibiotic choice for acute otitis media 2018. acute otitis media (AOM). The guidelines of the American Academy of Pediatrics It showed that by end of 2016,
2 Minute Medicine. Specialties. All [Policy Statement] New guidelines for pediatric acute otitis media released. March 4, 2013 2 Minute Medicine.
The following was adapted from the Canadian Paediatric Society’s statement on the “Management of Acute Otitis Media”. Please see the full statement for the full
Low quality evidence indicated that children treated with oral antibiotics were less likely to have acute otitis media (ear infection) episodes (CENTRAL 2016,
Updated Clinical Practice Guideline Otitis Media with
Antibiotic therapy for children with acute otitis media
Effective Treatment for Acute Otitis Externa. Meghan June 01, 2016. rare since the introduction of antibiotics for the treatment of acute otitis media,
Complications of Acute Otitis Media Red flags . Acute otitis media (AOM) in the presence of: Sepsis with post auricular swelling; Cranial nerve palsy
Guideline Summary Nicole Le Saux, Immunization Committee. Paediatr Child Health 2016;21(1) of Acute Otitis Media in Children Six Months of Age and Older”.
Systemic corticosteroids for acute otitis media in children. Acute otitis media clinical practice guideline defines AOM as an “acute onset of middle ear
2014-02-28 · Two-thirds of all children have an episode of acute otitis media An S2 guideline for the treatment of acute purulent otitis media is
Acute otitis media – Guidelines PediaMCU. February 16, 2016. Clinical practice guideline: the diagnosis and management of acute otitis media .
Clinical Practice Guideline: Otitis Media with Effusion (Update) Otolaryngology– Head and Neck Surgery 2016, Vol. 154(1S) Acute otitis media
Acute Otitis Media Red flags . Acute Unwell young children with discharging ears (acute suppurative otitis media) Acute Otitis Media. NICE Guideline 69.
Innovative technologies in diagnosing acute otitis media
Systemic corticosteroids for acute otitis media in
Recurrent acute otitis media Guideline The Diagnosis and Management of for Acute Otitis Media in Young Children. N Engl J Med 2016; 375
What is acute otitis media? – at least one symptom or finding indicative Diagnosis and Management of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis: 2013 AAP Guideline – Prepared for
There is still some debate whether antibiotics influence the short term outcome of acute otitis media. erythromycin is an alternative for penicillin allergic patients
ABSTRACTNew guidelines for managing acute otitis media include stricter criteria for properly diagno
Low quality evidence indicated that children treated with oral antibiotics were less likely to have acute otitis media (ear infection) episodes (CENTRAL 2016,
2018-04-13 · In the United States, acute otitis media Acute Otitis Media Guidelines. Pediatrics. 2016 Mar 28.
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media abstract This evidence-basedclinical practiceguideline isarevision of the2004
Management of acute otitis media in children six months Health. 2016 Jan-Feb health/practitioner-professional-resources/bc-guidelines/otitis-media
Guidelines by Alphabetical Listing. Otitis Media: Otitis Media – Acute Otitis Media & Otitis Media with Effusion For the latest updates on BC Guidelines,
Diagnosis requires acute onset and an abnormal ear examination with signs of middle ear inflammation and middle ear effusion. Avoid the routine use of antibiotic treatment for acute otitis media. Background. Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common problem in early childhood . 75% of children have at least one episode by school age
Acute Infection Guideline Summary TRIC 2016-17 Reference Articles Otitis Media: 1. Lieberthal AS et al. The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media.
Effective Treatment for Acute Otitis Externa. Meghan June 01, 2016. rare since the introduction of antibiotics for the treatment of acute otitis media,
Acute otitis externa (2016) Canadian Paediatric Society
Otitis media with effusion (glue ear) ebm-guidelines.com
Evidence-based information on guidelines of otitis media from hundreds of of the 2004 acute otitis media (AOM) guideline from the 01 August 2016.
2016-03-15 · Richard M. Rosenfeld, MD, MPH discusses OME – What it is, who it affects and information about the updated clinical practice guideline.
Diagnosis requires acute onset and an abnormal ear examination with signs of middle ear inflammation and middle ear effusion. Avoid the routine use of antibiotic treatment for acute otitis media. Background. Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common problem in early childhood . 75% of children have at least one episode by school age
2 Minute Medicine. Specialties. All [Policy Statement] New guidelines for pediatric acute otitis media released. March 4, 2013 2 Minute Medicine.
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media abstract This evidence-basedclinical practiceguideline isarevision of the2004
The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM is an infection of abrupt onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present.
Guideline Summary Nicole Le Saux, Immunization Committee. Paediatr Child Health 2016;21(1) of Acute Otitis Media in Children Six Months of Age and Older”.
ANMC Pediatric Acute Otitis Media (AOM) Treatment Guidelines Diagnosis Criteria Severe Symptoms Observation Criteria ANMC GAS Pharyngitis Guideline 2016 Author:
Acute Infection Guideline Summary TRIC 2016-17 Reference Articles Otitis Media: 1. Lieberthal AS et al. The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media.
Recurrent acute otitis media Guideline The Diagnosis and Management of for Acute Otitis Media in Young Children. N Engl J Med 2016; 375
Antibiotic choice for acute otitis media 2018. acute otitis media (AOM). The guidelines of the American Academy of Pediatrics It showed that by end of 2016,
Acute otitis media — entsho.com
ANTIMICROBIAL PRESCRIBING GUIDELINES IN GENERAL PRACTICE
Evidence-based recommendations on an antimicrobial prescribing strategy for acute otitis media 2016). More common complications of acute guideline on
Acute otitis media — Acute otitis media (AOM) is an acute illness marked by the presence of middle ear fluid and inflammation of the mucosa that lines the middle ear space . The infection is often caused by obstruction of the eustachian tube, which results in fluid retention and suppuration of retained secretions.
Acute otitis media – Guidelines PediaMCU. February 16, 2016. Clinical practice guideline: the diagnosis and management of acute otitis media .
After acute otitis media, EBM Guidelines. Dec 16, 2016 • Latest change Dec 16, 2016. Tuomas Klockars and Aino Ruohola. Table of contents.
2014-02-28 · Two-thirds of all children have an episode of acute otitis media An S2 guideline for the treatment of acute purulent otitis media is
Management of acute otitis media in children six months Health. 2016 Jan-Feb health/practitioner-professional-resources/bc-guidelines/otitis-media
Otitis media with effusion (OME) The presence of fluid in the middle ear without signs or symptoms of acute ear infection. Chronic OME OME persisting for 3 mo from the date of onset (if known) or from the date of diagnosis (if onset is unknown). Acute otitis media (AOM) The rapid onset of signs and symptoms of inflammation of the middle ear.
Acute Infection Guideline Summary TRIC 2016-17 Reference Articles Otitis Media: 1. Lieberthal AS et al. The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media.
Otitis media with effusion (glue ear) ebm-guidelines.com
antibiotics in acute otitis media General Practice Notebook