Acute otitis media guidelines pdf
20 min readAcute otitis media guidelines pdf
10/01/2014 · Acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion are common childhood disorders, a source of significant morbidity, and a leading cause of antibiotic prescription in primary health care. Although effective treatments are available, some shortcomings …
Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common disease occurring in infants and children and has major medical, social and economic effects. If we consider the Italian pediatric population and the incidence rates in different age ranges it can be calculated that almost …
Acute Otitis Media Guidelines in Selected Developed and Developing Countries: Uniformity and Diversity Article in Archives of Disease in Childhood · August 2016 DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2016-310729 CITATIONS 0 READS 29 4 authors: Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects: Acute otitis media guidelines View project The effect of tinnitus on the …
Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common infection for which antibacterial agents are prescribed for children in the United States. As such, the diagnosis and management of AOM has a
PDF version: The Recommendations for Clinical Care Guidelines on the Management of Otitis Media in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Populations (2010) (PDF 1227 KB) To obtain a hardcopy of the kit and associated products please contact National Mailing and Marketing at health@nationalmailing.com.au or phone 1800 020103 (quote: NMM code OT0270).
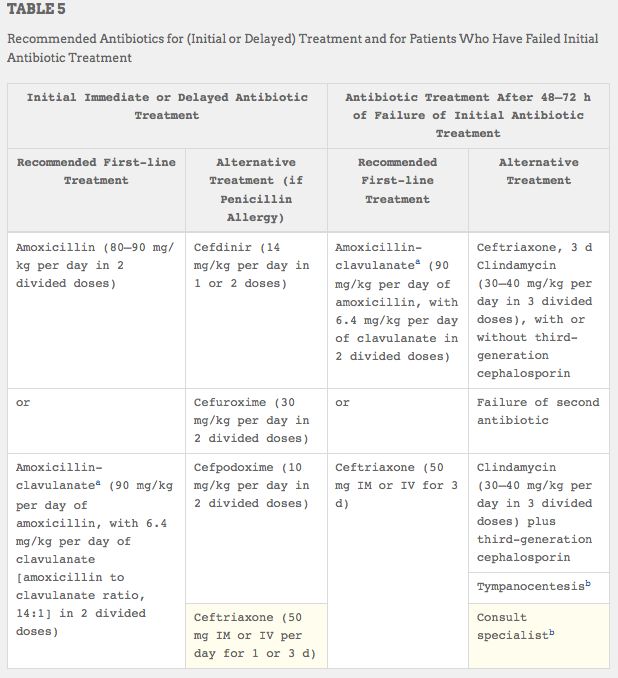
Otitis Media, Tympanostomy Tubes, and Clinical Practice Guidelines from 2013 Condition CPG Key Action Statement Discussion Points RECURRENT ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA (AOM) AAP Clinical Practice Guideline on Acute Otitis Media1 Clinicians MAy offer tympanostomy tubes for recurrent AOM (three episodes in six months or four episodes in one year with one episode in the preceding six months). …
All guidelines recommend oral amoxicillin as first-line therapy for acute otitis media The optimal physical finding to differentiate OME from AOM is tympanic membrane position. Patients with AOM have a bulging tympanic membrane; those with OME have …
The most important conditions are acute otitis media without perforation, acute otitis media with perforation, otitis media with effusion and chronic suppurative otitis media (see Table 1). There is currently a lack of consistency in definitions of different forms of otitis media (especially acute otitis media).
Acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion Clinical Practice Guidelines and Protocols in British Columbia. Otitis media: acute otitis media and otitis media …
13/04/2018 · In the United States, acute otitis media (AOM), defined by convention as the first 3 weeks of a process in which the middle ear shows the signs and symptoms of acute inflammation, is the most common affliction necessitating medical therapy for children younger than 5 …
This guideline sets out an antimicrobial prescribing strategy for acute otitis media (ear infection). It aims to limit antibiotic use and reduce antimicrobial resistance. Acute otitis media can be caused by viruses or bacteria. It lasts for about a week, and most children get better in 3 days without antibiotics. Serious complications are rare.
The AAP guidance provides the most recent evidence-based guidelines in the management of acute otitis media. It is intended to provide a framework for the management of children with AOM but must be taken in context with previous national guidance in the UK.
The 2013 AAP Guideline on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media emphasizes the need for accurate diagnosis, using strict otoscopic criteria for sound clinical decision-making.
Acute Otitis Media. Otolaryngology JAMA JAMA Network
Pediatric Acute OTITIS Media bccnp.ca
In a recent commentary, R.A.M.J. Damoiseaux1 misquotes the guideline for the treatment of otitis media that has been endorsed by the Guidelines Advisory Committee (GAC) of the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care and the Ontario Medical Association.
ANMC Pediatric Acute Otitis Media (AOM) Treatment Guidelines Diagnosis Criteria Severe Symptoms Observation Criteria New onset of otorrhea (not related to AOE)
Adherence to acute otitis media treatment guidelines among primary health care providers in Israel Noa Shviro-Roseman, Haim Reuveni, Eli Gazala, Eugene Leibovitz ∗ Division of Pediatrics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel
Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common condition seen in primary care offices, as 1 in 4 children will have at least 1 episode of AOM by age 10 years. 1 AOM results from infection of fluid that has become trapped in the middle ear.
Findings on Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Children with Recurrent Otitis Media 119 Findings on Prevention of Acute Otitis Media in Children with Recurrent Otitis Media .. 123
Guidelines for clinical care: Otitis Media. Rating (out of 4): Scope This guideline is intended for all physicians who deal with patients with otitis media. Diagnosis • Acute Otitis media. AOM is an acute, symptomatic inflammation of the ear with fluid behind the eardrum. • Causes. Either a bacterial infection or a viral infection of the ear can cause AOM • Fluid without inflammation-URI
Organizational Principles to Guide and Define the Child Health Care System and/or Improve the Health of all ChildrenCLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINEThe Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis …
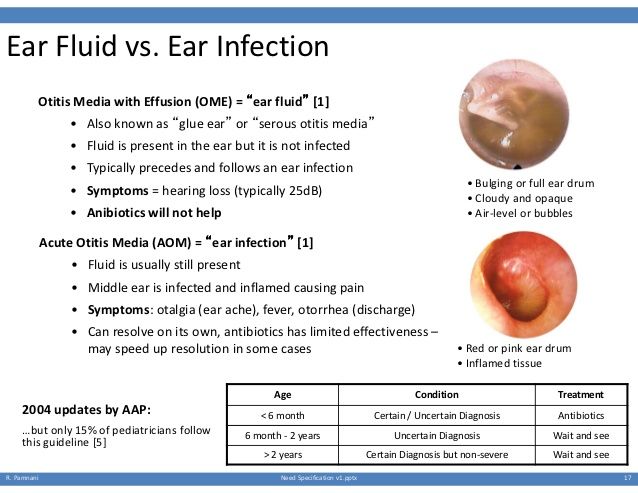
Comparison of otitis media with effusion (top) and acute otitis media (bottom). The left images show the appearance of the eardrum on otoscopy, and the right images depict the middle ear space. For otitis media with effusion, the middle ear space is filled with mucus or liquid (top right). For acute otitis media, the middle ear space is filled with pus, and the pressure causes the eardrum to
This evidence-based clinical practice guideline is a revision of the 2004 acute otitis media (AOM) guideline from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and …
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) Evidence Report. In preparing for the 2004 American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines, the AHRQ funded and conducted an exhaustive review of the literature on diagnosis and management of acute otitis media (AOM).
-A PAGE 2| Introduction To The Guidelines: Acute Otitis Media PAGE 3| Assessment Of The Guideline Methodology PAGE 4| Selected Guideline Recommendations,
General Guideline Title The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media. Bibliographic Source(s) Lieberthal AS, Carroll AE, Chonmaitree T, Ganiats TG, Hoberman A, Jackson MA, Joffe MD, Miller DT, Rosenfeld RM, Sevilla XD, Schwartz RH, Thomas PA, Tunkel DE.
Wait-and-see prescription for the treatment of acute otitis media: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006 Sep 13;296(10):1235-41. JAMA. 2006 Sep 13;296(10):1235-41. ↑ Hoberman A et al. Shortened Antimicrobial Treatment for Acute Otitis Media in Young Children.
Acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion Published by: Clinical Practice Guidelines and Protocols in British Columbia
Acute otitis media is the most frequently diagnosed bacterial infection in children. Over the past 2 decades, there has been no substantial change in the main bacterial pathogens that cause AOM, which are similar in both adults and children.
Otitis media: a common childhood illness. 26 BPJ Issue 46 acute otitis media have spontaneous resolution within two to 14 days.2 Paracetamol is the first-line analgesic. Ibuprofen is known to reduce inflammation and pain associated with acute otitis media, however, it should not be given if the child displays signs of dehydration or has concurrent asthma (NSAIDs can potentially worsen asthma
Acute otitis media (AOM) is defined as the presence of inflammation in the middle ear accompanied by the rapid onset of signs and symptoms of an ear infection. 1 Otitis media with effusion (OME) is defined as the presence of fluid in the middle ear without signs and symptoms of an ear infection.
Rosenfeld et al Clinical Practice Guideline: Acute Otitis Externa S5 common in chronic otitis externa or after treatment of AOE with topical, or 13less often systemic, antibiotics.
This guideline provides recommendations to clinicians for the management of children from 6 months through 12 years of age with uncomplicated acute otitis media (AOM). It addresses the appropriate diagnosis and initial
Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is the result of an initial episode of acute otitis media and is characterized by a persistent discharge from the middle ear through a tympanic perforation.
· Guidelines for children with acute otitis media (AOM) and Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) living in urban areas have been developed over the past few years (1) . · Children living in urban areas are generally treated by general practitioners whereas those living in rural
Background Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common childhood disease, with an enormous economic and healthcare-related burden. Guidelines and consensus papers for AOM diagnosis and management were published in many countries. Our objective was to study the differences and similarities between these protocols in developing and developed countries.
Otitis media (OM) is one of the most common infections in children. The cause can be viral, but is most often bacterial. 1 It remains one of the most common reasons for antibiotic prescribing for children. 2 Many episodes of acute OM are self-limiting and resolve without treatment, but antibiotics are often prescribed because these infections
Acute otitis media WikEM
Acute otitis media is an infection and is different than otitis media with effusion, the presence of fluid in the middle ear without infection. The November 17, 2010, issue of JAMA includes an article about diagnosis and treatment of acute otitis media.
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media abstract This evidence-basedclinical practiceguideline isarevision of the2004
Acute Otitis Media: Traditionally all acute otitis media has been treated with antibiotics. However, evidence would suggest that this at best shortens the duration of the pain by less than a day, and does not reduce the recurrence rate nor the complication rate of acute otitis media.
Acute otitis media (AOM), a common condition in children, is a closed space inflammatory process in the middle ear. It is more frequent in the first 2 years of life, due to the immaturity of
Paediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines The SA Paediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines are designed to assist clinicians with decisions about appropriate health care for children and young people aged 0-18 years, not including management of neonatal conditions.
The Interpretation section of the abstract in an article by Nicole Le Saux and associates1 reads as follows: “Our results did not support the hy-
19/03/2018 · Otitis media (OM) is the second most common disease of childhood, after upper respiratory infection (URI). OM is also the most common cause for childhood visits to a physician’s office. OM is also the most common cause for childhood visits to a physician’s office.
Optima Health. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media (Ages 6 months to 12 years) Guideline History . Original Approve . Date 08/94 Review/Revise
Infants and Children: Otitis Media Acute Management of Sore Ear: second edition Algorithm Assessment and Initial Management of Otitis Media * Avoid use in patients with pre-existing illnesses that may contribute to development of renal failure such as children with suspected or proven Gr A streptococcal infection.
What are the signs of Otitis Media? Acute Otitis Media (AOM) is when the ear is painful, or if the doctor looks into the ear and finds the ear drum is bulging with pus. This is an infection that needs antibiotics. Signs include: problems that need treatmentEar ache or pain in the ear – social media network marketing pdf 1 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media (AOM) in Children in Japan Subcommittee of Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Acute
acute otitis media is a self-limiting infection that mainly affects children acute otitis media can be caused by viruses and bacteria, and it is difficult to distinguish between these (both are often present at …
Acute otitis media (AOM) continues to be a common infection in young children. Milder disease, usually due to viruses or less virulent bacteria, resolves equally quickly with or without antibiotics. A bulging tympanic membrane, especially if yellow or hemorrhagic, has a high sensitivity for AOM that is likely to be bacterial in origin and is a
The guideline was published as a supplement in the February 2016 issue of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. The purpose of this multidisciplinary guideline is to identify quality improvement opportunities in managing otitis media with effusion (OME) and to create explicit and actionable recommendations to implement these opportunities in clinical practice.
Acute otitis media (AOM) is diagnosed on the basis of acute onset of pain and fever; a red, bulging tympanic membrane; and middle ear effusion. AOM is managed with analgesia (paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
The guideline, Otitis Media with Effusion, was updated by the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgeons and endorsed by the American Academy of Family Physicians.
The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media: American Academy of Pediatrics Guidelines 2013 Joe Grainger, Somiah Siddiq Department of ENT, Birmingham
Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common condition seen in primary care offices, as 1 in 4 children will have at least 1 episode of AOM by age 10 years. 1 x 1 Majeed, A. and Harris, T. Acute otitis media …
This evidence-based clinical practice guideline is a revision of the 2004 acute otitis media (AOM) guideline from the American Academy of Pediatrics(AAP) and American Academy of Family Physicians. Read Summary
The purpose of this guidance is to assist sponsors in the clinical development of drugs for the treatment of acute bacterial otitis media (ABOM).
Background Clinical practice guidelines focusing on judicious use of antibiotics for childhood acute otitis media (AOM) have been introduced in many countries around the world. Objective To systematically review the effects of these guidelines on the …
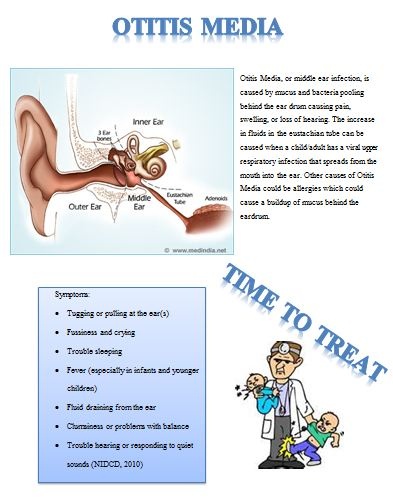
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM is an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating
Remote Nursing ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Certified Practice Pediatric Decision Support Tool: PEDIATRIC ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA DEFINITION . An acute suppurative infection of the middle ear, often preceded by a viral upper respiratory tract
Background: Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common childhood disease, with an enormous economic and healthcare-related burden. Guidelines and consensus papers for …
CARE GUIDELINES ON OTITIS MEDIA. The original ‘Recommendations for Clinical Care Guidelines on the Management of Otitis Media’ 1. were directly linked to the Systematic Review of Existing Evidence and Primary Care Guidelines on the Management of Otitis Media in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Populations (March 2001). 2. This updated version is based on the 2001 Guidelines …
Acute otitis media – Emergency management in children Purpose This document provides clinical guidance for all staff involved in the care and management of a child presenting to an Emergency Department (ED) with symptoms of acute otitis media (AOM) in Queensland. This guideline has been developed by senior ED clinicians and Paediatricians across Queensland, with input from senior staff …
Otitis media – a common childhood illness
GUIDELINE REVIEW The diagnosis and management of acute

OTITIS MEDIA Nursing and Midwifery – Flinders University
Otitis media Wikipedia

Acute Otitis Media Primary Care Clinics in Office Practice
(PDF) Acute Otitis Media Guidelines in Selected Developed
Impact of acute otitis media clinical practice guidelines
Otitis Media Guidelines AAP/AAFP Guidelines for Acute
– Otitis Media Information for Patients gacguidelines.ca
Otitis Media Acute Otitis Media (AOM) and Otitis Media

Acute otitis media Cancer Therapy Advisor
Guidelines for treating acute otitis media I CMAJ
Pediatric Acute OTITIS Media bccnp.ca
Acute otitis media Cancer Therapy Advisor
The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media: American Academy of Pediatrics Guidelines 2013 Joe Grainger, Somiah Siddiq Department of ENT, Birmingham
acute otitis media is a self-limiting infection that mainly affects children acute otitis media can be caused by viruses and bacteria, and it is difficult to distinguish between these (both are often present at …
Acute otitis media (AOM) is defined as the presence of inflammation in the middle ear accompanied by the rapid onset of signs and symptoms of an ear infection. 1 Otitis media with effusion (OME) is defined as the presence of fluid in the middle ear without signs and symptoms of an ear infection.
Acute otitis media (AOM) is diagnosed on the basis of acute onset of pain and fever; a red, bulging tympanic membrane; and middle ear effusion. AOM is managed with analgesia (paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Otitis Media, Tympanostomy Tubes, and Clinical Practice Guidelines from 2013 Condition CPG Key Action Statement Discussion Points RECURRENT ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA (AOM) AAP Clinical Practice Guideline on Acute Otitis Media1 Clinicians MAy offer tympanostomy tubes for recurrent AOM (three episodes in six months or four episodes in one year with one episode in the preceding six months). …
The AAP guidance provides the most recent evidence-based guidelines in the management of acute otitis media. It is intended to provide a framework for the management of children with AOM but must be taken in context with previous national guidance in the UK.
Optima Health. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media (Ages 6 months to 12 years) Guideline History . Original Approve . Date 08/94 Review/Revise
Paediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines The SA Paediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines are designed to assist clinicians with decisions about appropriate health care for children and young people aged 0-18 years, not including management of neonatal conditions.
The most important conditions are acute otitis media without perforation, acute otitis media with perforation, otitis media with effusion and chronic suppurative otitis media (see Table 1). There is currently a lack of consistency in definitions of different forms of otitis media (especially acute otitis media).
(PDF) Acute Otitis Media Guidelines in Selected Developed
acute otitis media.pdf General Guideline Title The
The guideline was published as a supplement in the February 2016 issue of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. The purpose of this multidisciplinary guideline is to identify quality improvement opportunities in managing otitis media with effusion (OME) and to create explicit and actionable recommendations to implement these opportunities in clinical practice.
19/03/2018 · Otitis media (OM) is the second most common disease of childhood, after upper respiratory infection (URI). OM is also the most common cause for childhood visits to a physician’s office. OM is also the most common cause for childhood visits to a physician’s office.
ANMC Pediatric Acute Otitis Media (AOM) Treatment Guidelines Diagnosis Criteria Severe Symptoms Observation Criteria New onset of otorrhea (not related to AOE)
General Guideline Title The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media. Bibliographic Source(s) Lieberthal AS, Carroll AE, Chonmaitree T, Ganiats TG, Hoberman A, Jackson MA, Joffe MD, Miller DT, Rosenfeld RM, Sevilla XD, Schwartz RH, Thomas PA, Tunkel DE.
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM is an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating
This evidence-based clinical practice guideline is a revision of the 2004 acute otitis media (AOM) guideline from the American Academy of Pediatrics(AAP) and American Academy of Family Physicians. Read Summary
Optima Health. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media (Ages 6 months to 12 years) Guideline History . Original Approve . Date 08/94 Review/Revise
Adherence to acute otitis media treatment guidelines among primary health care providers in Israel Noa Shviro-Roseman, Haim Reuveni, Eli Gazala, Eugene Leibovitz ∗ Division of Pediatrics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel
Clinical Practice Guideline – Acute Otitis Media with Effusion
Otitis media Wikipedia
· Guidelines for children with acute otitis media (AOM) and Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) living in urban areas have been developed over the past few years (1) . · Children living in urban areas are generally treated by general practitioners whereas those living in rural
Otitis media: a common childhood illness. 26 BPJ Issue 46 acute otitis media have spontaneous resolution within two to 14 days.2 Paracetamol is the first-line analgesic. Ibuprofen is known to reduce inflammation and pain associated with acute otitis media, however, it should not be given if the child displays signs of dehydration or has concurrent asthma (NSAIDs can potentially worsen asthma
13/04/2018 · In the United States, acute otitis media (AOM), defined by convention as the first 3 weeks of a process in which the middle ear shows the signs and symptoms of acute inflammation, is the most common affliction necessitating medical therapy for children younger than 5 …
Adherence to acute otitis media treatment guidelines among primary health care providers in Israel Noa Shviro-Roseman, Haim Reuveni, Eli Gazala, Eugene Leibovitz ∗ Division of Pediatrics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media abstract This evidence-basedclinical practiceguideline isarevision of the2004
What are the signs of Otitis Media? Acute Otitis Media (AOM) is when the ear is painful, or if the doctor looks into the ear and finds the ear drum is bulging with pus. This is an infection that needs antibiotics. Signs include: problems that need treatmentEar ache or pain in the ear
Acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion Clinical Practice Guidelines and Protocols in British Columbia. Otitis media: acute otitis media and otitis media …
acute otitis media is a self-limiting infection that mainly affects children acute otitis media can be caused by viruses and bacteria, and it is difficult to distinguish between these (both are often present at …
ANMC Pediatric Acute Otitis Media (AOM) Treatment Guidelines Diagnosis Criteria Severe Symptoms Observation Criteria New onset of otorrhea (not related to AOE)
Acute otitis media (AOM) is defined as the presence of inflammation in the middle ear accompanied by the rapid onset of signs and symptoms of an ear infection. 1 Otitis media with effusion (OME) is defined as the presence of fluid in the middle ear without signs and symptoms of an ear infection.
Paediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines The SA Paediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines are designed to assist clinicians with decisions about appropriate health care for children and young people aged 0-18 years, not including management of neonatal conditions.
All guidelines recommend oral amoxicillin as first-line therapy for acute otitis media The optimal physical finding to differentiate OME from AOM is tympanic membrane position. Patients with AOM have a bulging tympanic membrane; those with OME have …
Findings on Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Children with Recurrent Otitis Media 119 Findings on Prevention of Acute Otitis Media in Children with Recurrent Otitis Media .. 123
Acute otitis media – Emergency management in children Purpose This document provides clinical guidance for all staff involved in the care and management of a child presenting to an Emergency Department (ED) with symptoms of acute otitis media (AOM) in Queensland. This guideline has been developed by senior ED clinicians and Paediatricians across Queensland, with input from senior staff …
The purpose of this guidance is to assist sponsors in the clinical development of drugs for the treatment of acute bacterial otitis media (ABOM).
PAGE Updated Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Management
Otitis Media Information for Patients gacguidelines.ca
Background Clinical practice guidelines focusing on judicious use of antibiotics for childhood acute otitis media (AOM) have been introduced in many countries around the world. Objective To systematically review the effects of these guidelines on the …
Comparison of otitis media with effusion (top) and acute otitis media (bottom). The left images show the appearance of the eardrum on otoscopy, and the right images depict the middle ear space. For otitis media with effusion, the middle ear space is filled with mucus or liquid (top right). For acute otitis media, the middle ear space is filled with pus, and the pressure causes the eardrum to
The Interpretation section of the abstract in an article by Nicole Le Saux and associates1 reads as follows: “Our results did not support the hy-
Acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion Published by: Clinical Practice Guidelines and Protocols in British Columbia
Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common disease occurring in infants and children and has major medical, social and economic effects. If we consider the Italian pediatric population and the incidence rates in different age ranges it can be calculated that almost …
CARE GUIDELINES ON OTITIS MEDIA. The original ‘Recommendations for Clinical Care Guidelines on the Management of Otitis Media’ 1. were directly linked to the Systematic Review of Existing Evidence and Primary Care Guidelines on the Management of Otitis Media in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Populations (March 2001). 2. This updated version is based on the 2001 Guidelines …
This guideline sets out an antimicrobial prescribing strategy for acute otitis media (ear infection). It aims to limit antibiotic use and reduce antimicrobial resistance. Acute otitis media can be caused by viruses or bacteria. It lasts for about a week, and most children get better in 3 days without antibiotics. Serious complications are rare.
· Guidelines for children with acute otitis media (AOM) and Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) living in urban areas have been developed over the past few years (1) . · Children living in urban areas are generally treated by general practitioners whereas those living in rural
The 2013 AAP Guideline on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media emphasizes the need for accurate diagnosis, using strict otoscopic criteria for sound clinical decision-making.
The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media: American Academy of Pediatrics Guidelines 2013 Joe Grainger, Somiah Siddiq Department of ENT, Birmingham
Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common condition seen in primary care offices, as 1 in 4 children will have at least 1 episode of AOM by age 10 years. 1 x 1 Majeed, A. and Harris, T. Acute otitis media …
Acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion Clinical Practice Guidelines and Protocols in British Columbia. Otitis media: acute otitis media and otitis media …
Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common condition seen in primary care offices, as 1 in 4 children will have at least 1 episode of AOM by age 10 years. 1 AOM results from infection of fluid that has become trapped in the middle ear.
(PDF) The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media
national otitis media guidelines Department of Health
Acute otitis media (AOM) is diagnosed on the basis of acute onset of pain and fever; a red, bulging tympanic membrane; and middle ear effusion. AOM is managed with analgesia (paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Findings on Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Children with Recurrent Otitis Media 119 Findings on Prevention of Acute Otitis Media in Children with Recurrent Otitis Media .. 123
Background Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common childhood disease, with an enormous economic and healthcare-related burden. Guidelines and consensus papers for AOM diagnosis and management were published in many countries. Our objective was to study the differences and similarities between these protocols in developing and developed countries.
The 2013 AAP Guideline on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media emphasizes the need for accurate diagnosis, using strict otoscopic criteria for sound clinical decision-making.
Otitis Media, Tympanostomy Tubes, and Clinical Practice Guidelines from 2013 Condition CPG Key Action Statement Discussion Points RECURRENT ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA (AOM) AAP Clinical Practice Guideline on Acute Otitis Media1 Clinicians MAy offer tympanostomy tubes for recurrent AOM (three episodes in six months or four episodes in one year with one episode in the preceding six months). …
The guideline was published as a supplement in the February 2016 issue of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. The purpose of this multidisciplinary guideline is to identify quality improvement opportunities in managing otitis media with effusion (OME) and to create explicit and actionable recommendations to implement these opportunities in clinical practice.
Acute otitis media is an infection and is different than otitis media with effusion, the presence of fluid in the middle ear without infection. The November 17, 2010, issue of JAMA includes an article about diagnosis and treatment of acute otitis media.
Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common condition seen in primary care offices, as 1 in 4 children will have at least 1 episode of AOM by age 10 years. 1 AOM results from infection of fluid that has become trapped in the middle ear.
Paediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines The SA Paediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines are designed to assist clinicians with decisions about appropriate health care for children and young people aged 0-18 years, not including management of neonatal conditions.
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) Evidence Report. In preparing for the 2004 American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines, the AHRQ funded and conducted an exhaustive review of the literature on diagnosis and management of acute otitis media (AOM).
Organizational Principles to Guide and Define the Child Health Care System and/or Improve the Health of all ChildrenCLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINEThe Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis …
Acute otitis media (AOM) continues to be a common infection in young children. Milder disease, usually due to viruses or less virulent bacteria, resolves equally quickly with or without antibiotics. A bulging tympanic membrane, especially if yellow or hemorrhagic, has a high sensitivity for AOM that is likely to be bacterial in origin and is a
Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common disease occurring in infants and children and has major medical, social and economic effects. If we consider the Italian pediatric population and the incidence rates in different age ranges it can be calculated that almost …
guidelines of otitis media Evidence search NICE
PAGE Updated Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Management
1 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media (AOM) in Children in Japan Subcommittee of Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Acute
Background Clinical practice guidelines focusing on judicious use of antibiotics for childhood acute otitis media (AOM) have been introduced in many countries around the world. Objective To systematically review the effects of these guidelines on the …
CARE GUIDELINES ON OTITIS MEDIA. The original ‘Recommendations for Clinical Care Guidelines on the Management of Otitis Media’ 1. were directly linked to the Systematic Review of Existing Evidence and Primary Care Guidelines on the Management of Otitis Media in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Populations (March 2001). 2. This updated version is based on the 2001 Guidelines …
This evidence-based clinical practice guideline is a revision of the 2004 acute otitis media (AOM) guideline from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and …
Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common disease occurring in infants and children and has major medical, social and economic effects. If we consider the Italian pediatric population and the incidence rates in different age ranges it can be calculated that almost …
Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common infection for which antibacterial agents are prescribed for children in the United States. As such, the diagnosis and management of AOM has a

Background Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common childhood disease, with an enormous economic and healthcare-related burden. Guidelines and consensus papers for AOM diagnosis and management were published in many countries. Our objective was to study the differences and similarities between these protocols in developing and developed countries.
PAGE Updated Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Management
Guidelines for treating acute otitis media I CMAJ
AAFP/AAP Guidelines for Acute Otitis Media 2013 (pdf
The AAP guidance provides the most recent evidence-based guidelines in the management of acute otitis media. It is intended to provide a framework for the management of children with AOM but must be taken in context with previous national guidance in the UK.
Otitis Media Acute Otitis Media (AOM) and Otitis Media
ANMC Pediatric Acute Otitis Media (AOM) Treatment Guidelines
national otitis media guidelines Department of Health