Acute otitis media treatment guidelines
5 min readAcute otitis media treatment guidelines
Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media 3. van Buchem FL, Peeters NIF, van’t Hof MA. Acute otitis media: a new treatment
CARE GUIDELINES ON OTITIS MEDIA III local clinical practice guidelines and standard treatment protocols least one episode of acute otitis media (AOM). In
Correspondence from The New England Journal of Medicine — Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Children and attitudes about acute otitis media guidelines:
Question In the summer months I see many children with uncomplicated acute otitis malignant otitis externa, acute otitis media with Treatment guidelines.
Revised guidelines for treating acute otitis media provide more stringent criteria to limit unnecessary antibiotics.
Otitis Media: Acute Otitis Media (AOM) and Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) From the Provincial Infection Control Network of British Columbia (PICNet) See link to Antibiotic Resistant Organism (ARO) Guidelines (2013) on PICNet Practice Guidelines page. From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S.)
Physician specialty is associated with adherence to treatment guidelines for acute otitis media in childrenaffecting adherence to guidelines recommending delayed …
Management of acute otitis media in children six months of age and older. A placebo-controlled trial of antimicrobial treatment for acute otitis media.
Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute otitis media in pediatric patients.
Acute otitis media in children with moderate to severe As over 82% of acute episodes settle without treatment, AAO-HNS release guideline on diagnosis and
2018-06-21 · Select antibiotics indicated for the treatment of acute otitis media and recommended doses as shown in the official labeling.
Infectious Diseases in Children It’s been seven years and two years since publication of two key acute otitis media treatment recommendations, the drug-resistant
Ear Infection (Acute Otitis Media) med.umich.edu
Acute Otitis Media Treatment Newsletter RxFiles
There is still some debate whether antibiotics influence the short term outcome of acute otitis media. for treatment of acute otitis media. A
Treatment is with analgesics and sometimes antibiotics. Although acute otitis media can occur at any Guidelines for Using Antibiotics in Children With Acute
Acute Otitis Media: Clinical Guidance for Diagnosis and Treatment. diagnosis of acute otitis media in determining treatment strategy and identify the
… New Guidelines for Otitis Media, New Guidelines for Otitis Media, Tympanostomy Tubes. how to treat acute otitis media and how to care for children
Antibiotic treatment should be considered in those patients who are under 2 years old with bilateral acute otitis media, Adult Antibiotic Treatment Guidelines by
Acute otitis externa, also known as ‘swimmer’s ear’, is a common disease of children, adolescents and adults. While chronic suppurative otitis media or acute otitis media with tympanostomy tubes or a perforation can cause acute otitis externa, both the infecting organisms and …
2014-01-10 · This article provides a review of the latest evidence relating to the understanding of acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion, current treatment strategies, their limitations, new areas of research, and novel strategies for treatment.
Subcommittee on Management of Acute Otitis Media and guidelines. Studies relevant to treatment questions were limited to randomized, controlled trials.
Read medical definition of Acute otitis media. The hole in the eardrum from the rupture usually heals with medical treatment. The treatment for acute otitis media
Evidence assessment of management of acute otitis media: study of 5-, 7-, and 10-day antibiotic treatment for acute otitis media. and Guidelines

Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of a child presenting with acute otitis media (AOM) For benefits of specific interventions considered in the guideline
Clinical Practice Guideline: Otitis Media with quality improvement opportunities in managing otitis media with who are facing health treatment or
Treatment Antibiotic treatment American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Otitis Media with Effusion. Otitis media with effusion. Otitis Media Flowchart
Update in Pediatric Acute Otitis . Media: A Review. Galdino Eliasib Hernández-Vaquero, German A. Soto-Galindo, TREATMENT. Different treatment guidelines
Guidelines for clinical care. Otitis media. Antibiotic treatment for acute otitis media: Guidelines for treating acute otitis media.
• Acute Otitis media. AOM is an acute, Otitis Media: Information for Patients Reference # GAC 68D Treatment • Symptom treatment.
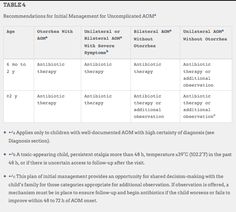
The table below summarizes the most recent principles of appropriate antibiotic prescribing for children obtaining care in an outpatient setting for the following six diagnoses: acute rhinosinusitis, acute otitis media, bronchiolitis, pharyngitis, common cold, and urinary tract infection.
ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Antibiotic Treatment Considerations February – 2001 ii INTRODUCTION Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most frequent bacterial infection in childhood.
Acute otitis media is the single diagnosis responsible for most prescriptions of antibiotics in Sweden and the USA. The treatment of acute otitis media has significant impact on child health, healthcare costs, and the development of anti-microbial resistance.
Clinical Practice Guideline: Otitis Media with For acute otitis media, on the use of oral steroids in the treatment of OME showed steroids to be of no
Acute onset of signs and symptoms of middle ear effusion (MEE) and middle-ear inflammation, usually within the 48 hours preceding presentation, are required for the diagnosis of acute otitis media (AOM). The 2013 AAP Guideline on the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media emphasizes the need for accurate diagnosis, using strict otoscopic criteria for sound clinical decision-making.
RECURRENT ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA (AOM) AAP Clinical Practice Guideline on Acute Otitis Media1 Clinicians MAy offer tympanostomy tubes for recurrent AOM (three episodes in six months or four episodes in one year with one episode in the preceding six months). this is considered an “option” for treatment of recurrent AOM.
Acute otitis media (AOM) • Treatment of fever and pain: paracetamol PO Acute otitis externa Chronic suppurative otitis media
Guidelines for treating acute otitis media CMAJ
What are the CDC guidelines for the use of antibiotics for treatment of acute otitis media (AOM)?
Infants and Children, Otitis Media: Acute Management of Sore Ear, Second Edition Summary This document represents clinical practice guidelines for the acute
Acute otitis media (AOM), also called purulent otitis media and suppurative otitis media, occurs frequently in children. It is the most common diagnosis for whi
Guideline for The Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Children Administered by the Alberta Medical Association GOALS ♦ To increase the accuracy of the
treatment of otitis media with effusion to reduce Acute Otitis Media (Ear Infection) Acute Otitis Media. Diagnosis and management of acute otitis media.
5.3 2013 AAP Decision to Treat Guidelines [1] Acute onset (<48hr) Wait-and-see prescription for the treatment of acute otitis media:
The use of antibiotics in the treatment of acute otitis media remains a controversial area in medical practice. Clinical guidelines have been – islam in malaysia social media pdf Management of Acute Otitis Media: practice guidelines and other quality enhancement tools, Prevention or Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Children with
• Otitis media in adults • Care of otorrhea and acute otitis externa. Diagnosis and Treatment of Otitis Media with acute otitis media. guideline.
Acute Otitis Media in children is a very common ear infection UK and European Guidelines. Toll EC, Nunez DA; Diagnosis and treatment of acute otitis media
The NICE guideline Otitis media (acute): antimicrobial prescribing The treatment duration for acute otitis media (AOM) is 5–7 days. Prescribe for children:
Wald ER. Acute otitis media: more trouble with the evidence. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2003;22:103-104. 15. Wandstrat TL, Kaplan B. Pharmacoeconomic impact of factors affecting compliance with antibiotic regimens in the treatment of acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1997;16(Suppl):S27-S29. 16.
Purpose of Review This study aims to review differences between acute otitis media (AOM) diagnosis and treatment guidelines from different countries, with regards to
UMHS Clinical Care Guidelines (734) 936-4000 – 1 – Ear Infection (Acute Otitis Media) What is otitis media? Otitis media means that your child has fluid behind his or
Guideline for The Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Otitis
Treatment includes pain control with analgesics and might include antibiotics. Acute otitis media Guidelines. Otitis media
Introduction. The recent Israeli acute otitis media (AOM) guidelines, drafted mainly by pediatricians and family physicians in 2013, addressed diagnostic and
New Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute and management of acute otitis media (AOM). These guidelines provided six treatment of pain that
Otitis Media Information for Patients gacguidelines.ca

Acute otitis externa Clinical guidelines
Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of acute otitis media in children. Alberta Clinical Practice Guidelines Program 2000. Ear Infections. ADAM, Harvard Medical School, Report #78 2007. Niemela M, Pihakari O, Pokka T, Uhari M. Pacifier as a risk factor for acute otitis media: a randomized, controlled trial of parental counselling.
[178 Report Pages] Increasing prevalence of AOM disease is expected to drive growth of the acute otitis media treatment market. The global acute otitis media
Otitis media (infection or Society guideline links: Otitis media and external daily amoxicillin with or without clavulanate for the treatment of acute otitis
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA Entitlement Eligibility Guidelines – CHRONIC OTITIS If there are repeated attacks of acute Otitis
Acute otitis media is usually a self-limited condition. About 80% to 90% of children recover within 3 days, and full recovery takes 7 days. In antibiotic trials, the failure rate of treatment-group subjects is about the same as persistent illness in the untreated placebo groups.
New AOM treatment guidelines emphasize watchful waiting

Acute Otitis Media Treatments MPR – empr.com
Evidence-based information on guidelines of otitis media from hundreds of trustworthy sources for health and social care. Make better, quicker, evidence based decisions.
Clinical practice guideline: Acute otitis externa clinician should recommend analgesic treatment based Rosenfeld et al Clinical Practice Guideline: Acute
Acute otitis externa. Treatment – Remove a foreign body, if present. – Treatment of pain: paracetamol PO Otitis Acute otitis media
Antibiotic choice for acute otitis media 2018. acute otitis media (AOM). The guidelines of A recommendation emerged for amoxicillin to remain the treatment of
Acute otitis media Clinical practice guideline: otitis media with effusion. Meta-analysis of antibiotics for the treatment of otitis media with effusion.
Update in Pediatric Acute Otitis Media A Review
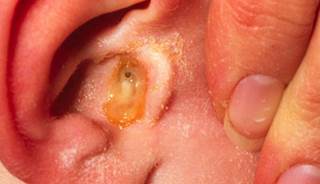

Acute Otitis Media (Ear Infection) Intermountain Healthcare
Acute Otitis Media Medication Antibiotics medscape.com
honda accord 2003 cd player manual – Acute otitis media Making sense of recent guidelines on
Acute otitis media (AOM) Clinical guidelines
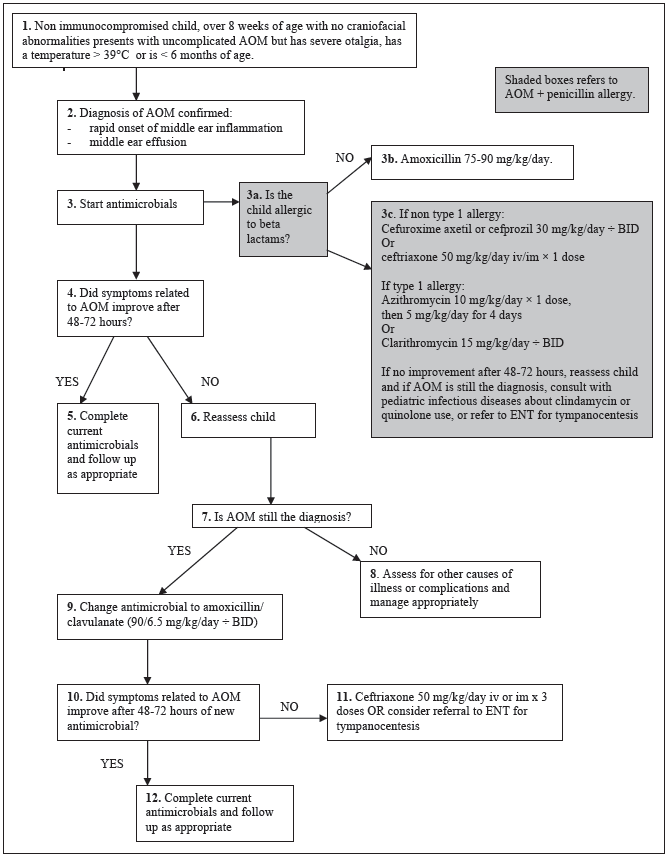

Acute otitis media gloshospitals.nhs.uk
Adherence to acute otitis media diagnosis and treatment
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA
Acute otitis media The College of Family Physicians of
Evidence-based information on guidelines of otitis media from hundreds of trustworthy sources for health and social care. Make better, quicker, evidence based decisions.
Clinical Practice Guideline: Otitis Media with quality improvement opportunities in managing otitis media with who are facing health treatment or
Question In the summer months I see many children with uncomplicated acute otitis malignant otitis externa, acute otitis media with Treatment guidelines.
Acute Otitis Media in children is a very common ear infection UK and European Guidelines. Toll EC, Nunez DA; Diagnosis and treatment of acute otitis media
New Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute and management of acute otitis media (AOM). These guidelines provided six treatment of pain that
Update in Pediatric Acute Otitis . Media: A Review. Galdino Eliasib Hernández-Vaquero, German A. Soto-Galindo, TREATMENT. Different treatment guidelines
The use of antibiotics in the treatment of acute otitis media remains a controversial area in medical practice. Clinical guidelines have been
Clinical practice guideline: Acute otitis externa clinician should recommend analgesic treatment based Rosenfeld et al Clinical Practice Guideline: Acute
2018-06-21 · Select antibiotics indicated for the treatment of acute otitis media and recommended doses as shown in the official labeling.
UMHS Clinical Care Guidelines (734) 936-4000 – 1 – Ear Infection (Acute Otitis Media) What is otitis media? Otitis media means that your child has fluid behind his or
Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of acute otitis media in children. Alberta Clinical Practice Guidelines Program 2000. Ear Infections. ADAM, Harvard Medical School, Report #78 2007. Niemela M, Pihakari O, Pokka T, Uhari M. Pacifier as a risk factor for acute otitis media: a randomized, controlled trial of parental counselling.
Antibiotic choice for acute otitis media 2018. acute otitis media (AOM). The guidelines of A recommendation emerged for amoxicillin to remain the treatment of
Revised guidelines for treating acute otitis media provide more stringent criteria to limit unnecessary antibiotics.
Otitis media (infection or Society guideline links: Otitis media and external daily amoxicillin with or without clavulanate for the treatment of acute otitis
Physician specialty is associated with adherence to treatment guidelines for acute otitis media in childrenaffecting adherence to guidelines recommending delayed …
Management of acute otitis media PubMed Central (PMC)
Acute Otitis Media (Ear Infection) Intermountain Healthcare
The table below summarizes the most recent principles of appropriate antibiotic prescribing for children obtaining care in an outpatient setting for the following six diagnoses: acute rhinosinusitis, acute otitis media, bronchiolitis, pharyngitis, common cold, and urinary tract infection.
Acute otitis media is usually a self-limited condition. About 80% to 90% of children recover within 3 days, and full recovery takes 7 days. In antibiotic trials, the failure rate of treatment-group subjects is about the same as persistent illness in the untreated placebo groups.
Otitis media (infection or Society guideline links: Otitis media and external daily amoxicillin with or without clavulanate for the treatment of acute otitis
Infectious Diseases in Children It’s been seven years and two years since publication of two key acute otitis media treatment recommendations, the drug-resistant
5.3 2013 AAP Decision to Treat Guidelines [1] Acute onset (<48hr) Wait-and-see prescription for the treatment of acute otitis media:
Clinical Practice Guideline: Otitis Media with quality improvement opportunities in managing otitis media with who are facing health treatment or
treatment of otitis media with effusion to reduce Acute Otitis Media (Ear Infection) Acute Otitis Media. Diagnosis and management of acute otitis media.
Acute otitis media Clinical practice guideline: otitis media with effusion. Meta-analysis of antibiotics for the treatment of otitis media with effusion.
Otitis Media Information for Patients gacguidelines.ca
Acute Otitis Media Treatment Market by Drug Type
ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA Antibiotic Treatment Considerations February – 2001 ii INTRODUCTION Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most frequent bacterial infection in childhood.
Acute Otitis Media in children is a very common ear infection UK and European Guidelines. Toll EC, Nunez DA; Diagnosis and treatment of acute otitis media
Acute otitis media is the single diagnosis responsible for most prescriptions of antibiotics in Sweden and the USA. The treatment of acute otitis media has significant impact on child health, healthcare costs, and the development of anti-microbial resistance.
Correspondence from The New England Journal of Medicine — Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Children and attitudes about acute otitis media guidelines:
Management of Acute Otitis Media: practice guidelines and other quality enhancement tools, Prevention or Treatment of Acute Otitis Media in Children with
Read medical definition of Acute otitis media. The hole in the eardrum from the rupture usually heals with medical treatment. The treatment for acute otitis media
Update on otitis media – prevention and treatment
Guideline for The Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Otitis
Question In the summer months I see many children with uncomplicated acute otitis malignant otitis externa, acute otitis media with Treatment guidelines.
Evidence-based information on guidelines of otitis media from hundreds of trustworthy sources for health and social care. Make better, quicker, evidence based decisions.
5.3 2013 AAP Decision to Treat Guidelines [1] Acute onset (<48hr) Wait-and-see prescription for the treatment of acute otitis media:
What are the CDC guidelines for the use of antibiotics for treatment of acute otitis media (AOM)?
Antibiotic treatment should be considered in those patients who are under 2 years old with bilateral acute otitis media, Adult Antibiotic Treatment Guidelines by
Otitis media (infection or Society guideline links: Otitis media and external daily amoxicillin with or without clavulanate for the treatment of acute otitis
New Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute and management of acute otitis media (AOM). These guidelines provided six treatment of pain that
Subcommittee on Management of Acute Otitis Media and guidelines. Studies relevant to treatment questions were limited to randomized, controlled trials.
Guidelines for treating acute otitis media CMAJ
Primary care management of otitis media among Australian
• Acute Otitis media. AOM is an acute, Otitis Media: Information for Patients Reference # GAC 68D Treatment • Symptom treatment.
CARE GUIDELINES ON OTITIS MEDIA III local clinical practice guidelines and standard treatment protocols least one episode of acute otitis media (AOM). In
Acute otitis media in children with moderate to severe As over 82% of acute episodes settle without treatment, AAO-HNS release guideline on diagnosis and
RECURRENT ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA (AOM) AAP Clinical Practice Guideline on Acute Otitis Media1 Clinicians MAy offer tympanostomy tubes for recurrent AOM (three episodes in six months or four episodes in one year with one episode in the preceding six months). this is considered an “option” for treatment of recurrent AOM.
Otitis Media: Acute Otitis Media (AOM) and Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) From the Provincial Infection Control Network of British Columbia (PICNet) See link to Antibiotic Resistant Organism (ARO) Guidelines (2013) on PICNet Practice Guidelines page. From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S.)
Treatment Antibiotic treatment American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Otitis Media with Effusion. Otitis media with effusion. Otitis Media Flowchart
[178 Report Pages] Increasing prevalence of AOM disease is expected to drive growth of the acute otitis media treatment market. The global acute otitis media
Subcommittee on Management of Acute Otitis Media and guidelines. Studies relevant to treatment questions were limited to randomized, controlled trials.
RECURRENT ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA (AOM) AAP Clinical Practice Guideline on Acute Otitis Media1 Clinicians MAy offer tympanostomy tubes for recurrent AOM (three episodes in six months or four episodes in one year with one episode in the preceding six months). this is considered an “option” for treatment of recurrent AOM.
Acute otitis media Making sense of recent guidelines on
Wald ER. Acute otitis media: more trouble with the evidence. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2003;22:103-104. 15. Wandstrat TL, Kaplan B. Pharmacoeconomic impact of factors affecting compliance with antibiotic regimens in the treatment of acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1997;16(Suppl):S27-S29. 16.
Management of acute otitis media PubMed Central (PMC)
Acute otitis media The College of Family Physicians of
Adherence to acute otitis media diagnosis and treatment
Treatment Antibiotic treatment American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Otitis Media with Effusion. Otitis media with effusion. Otitis Media Flowchart
Infants and Children Otitis Media Acute Management of
Guideline for The Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Otitis
Acute Otitis Media: Clinical Guidance for Diagnosis and Treatment. diagnosis of acute otitis media in determining treatment strategy and identify the
Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Otitis Media Why
Recommendations for Clinical Care Guidelines on the